161 Grounding and Shielding Techniques for EMI, EMC and ESD
Applications In modern electronics, as component size continues to decrease and complexity to increase, electrostatic and magnetic fields and their interactions are becoming increasingly important. As problems have arisen, creative solutions have been developed. This course pulls together the latest tools and techniques for overcoming problems related to electrostatic and magnetic coupling. An understanding of the principles and recent developments in this growing field is essential to many individuals in both the commercial and military electronics industries.
For Whom Intended This course is intended for individuals whose work requires an understanding of the effects of interacting electrostatic and magnetic fields on electrical and electronic equipment. Circuit designers, electronics packaging specialists, systems engineers, and electronic test specialists will find this course helpful.
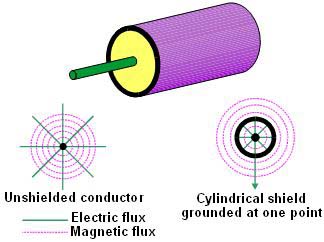 Objectives To help participants to understand grounding and shielding concepts and terminology. To provide an overview of the newest and most effective techniques for overcoming problems through the proper use of grounds and shields.
Objectives To help participants to understand grounding and shielding concepts and terminology. To provide an overview of the newest and most effective techniques for overcoming problems through the proper use of grounds and shields.
Brief Course Description The course is not an in-depth electrical engineering course but rather is aimed at individuals who require an intensive overview of basic principals, potential pitfalls and practical techniques, without the assumption of much prior knowledge of the topic.
The course is fast paced and as non-mathematical as possible. It begins with a review of electrostatic concepts, such as charges, fields and forces. It then takes up the basic theory of electrostatic and electromagnetic fields and field coupling. Armed with an understanding of the problem-causing mechanisms, students are prepared to devise solutions. The course addresses practical considerations such as cabling choices and the proper design and use of grounds. Effective grounding and shielding of amplifiers, voltmeters and enclosures will be covered. Techniques for measuring shielding effectiveness will be addressed. Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) will be covered as it relates to equipment design. Comprehensive units on circuit board layout and switching power supplies conclude the course.
Bonus Chapter Chapter 8, "Guarded Voltmeter" is shown in the course outline below, but it is not presented in the classroom, and it is not included in the Complete Video Course. However, it is provided in the course materials for self-study by interested students, and may be included in on-site presentations at the client's request.
Diploma Programs This course is required for TTi's Data Acquisition & Analysis Specialist (DAAS), Electronic Design Specialist (EDS), Electronic Telecommunications Specialist (ETS), Instrumentation Test Specialist (ITS) and Metrology Calibration Specialist (MCS) Diploma Programs and is an optional course for any other TTi specialist certificate program.
Prerequisites Students should have completed TTi’s course no. 104, Electronics for Non-Electronic Engineers or the equivalent. This course is aimed toward individuals actively involved in related technical fields. An understanding of basic electrical theory is required.
Text Each student will receive 180 days access to the on-line electronic course workbook. Renewals and printed textbooks are available for an additional fee.
Course Hours, Certificate and CEUs Class hours/days for on-site courses can vary from 14-35 hours over 2-5 days as requested by our clients. Upon successful course completion, each participant receives a certificate of completion and one Continuing Education Unit (CEU) for every ten class hours.
Internet Complete Course 161 features over 13 hours of video as well as more in-depth reading material. All chapters of course 161 are also available as OnDemand Internet Short Topics. See the course outline below for details.
Course Outline
Chapter 1A - Definitions, Terminology and Basic Concepts of EMI/EMC/ESD
- Electromagnetic Interference Transmission
- EMI and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
- Examples of EMI
- Electrical Noise Sources
- Types of Interference
- EED—Electro-Explosive Device
- Disturbances on the Main Supply
- Additional Electromagnetic Interference
- Software
- Modern-Day Electronics
- EMC: Electromagnetic Compatibility
- What Can Cause Interference?
- Field Reduction
- Primary Cause of Interference—Overload
- Schematic Information
- Details of Layout
- Components
Chapter 1B - Electrostatics
- Electrical Fundamentals
- Electrostatic Field and Potentials
- Electrical Charge
- Conductors and Insulators
- Measuring Current
- Resistance
- Voltage
- Ohm's Law
- Electric Charge
- Electrostatic Force
- Electrostatic Field Strength
- Potential Difference (Voltage)
- Spherical Conductor with a Charge
- Capacitive Charge
- Capacitance
- Relative Permittivity (Dielectric Constant)
- Field Representations
Chapter 2 - Electric Fields
- Capacitance
- Capacitance and Energy Storage
- Self and Mutual Capacitance
- Electric Shielding
- Energy in a Single Capacitor
- Nonconductive Coupling
- Crosstalk
- Electric Fields
- Electric-Field Coupling
- Capacitive Coupling
- Coupled Response
- Low-Frequency Model
- Crosstalk from Pulses
- Capacitance Between Two Wires in Space
- Approximate Trace-to-Trace Capacitance
- Using a Ground Trace
- Adding a Ground Plane
- Electrostatic Shielding
- Voltage Sources
- Earth Plane
- Room Pickup
Chapter 3 - Magnetic Field Coupling
- Magnetic Fields
- Solenoid
- Inductance and Energy Storage
- Small-Loop Approximation
- Magnetic Coupling Between Lines
- Mutual Inductance
- Depends on Loop Area
- Between Two Wires
- Ground Plane--Wire Position
- Orientation
- Coupling Between Inductors
- High-(mu) Material
- Inductors
- Magnetic Fields Created by Current Flow
Chapter 4 - Mixed Coupling
- Effect of Impedance on Coupling Type
- Dual Analysis
- Superposition Model (low frequencies)
- Equivalent Circuit
- Application of Superposition
- Coupled Response
- Extended Model
- Time Constants
- Typical Response
- Lines Terminated in Characteristic Impedance
- Effect of Line-Termination Impedances
Chapter 5 - Cables
- Magnetic Coupling into a Loop
- Twisted Pair
- Ribbon Cables
- Large Mutual Inductance—Lines Close Together
- Small Mutual Inductance—Lines Farther Apart
- Effect of Poor Cable Grounding
- Ground Current
- Shielding
- Shielded Capacitive Coupling
- Coupled Response
- Proper Termination of Shield
- Conductor Shielding
- Magnetic Field Produced by Current
- Single-Point Ground
- Magnetic Shield Carries Return Current
- Alternate Current Paths
- Magnetic Coupling Between Shield and Center Conductor
- Shield Cutoff
- Shield Loop Analysis
- Ground Current
- Effectiveness of Various Methods
- Poor Shield Grounding
- High-Frequency Current Flow
- Poor Grounding Causes External Shield Current
- Ferrite Choke Raises Z[sub]ex
- Measuring Common-Mode Currents on Cables
- Level of Allowed Current on Cables
- Common-Mode Current Measurement Procedure
- Coaxial Cable vs. Twisted Pair
Chapter 6 - Grounding
- What is a Ground?
- Types of Grounds
- Grounding Effectiveness
- Grounds—Three Wire Outlet
- AC Power Distribution
- Key Words in the Power Industry
- Laboratory Practice-Safety
- Safety
- Grounds
- Signal Grounds
- Single Point Grounds
- Single-Point Ground Systems
- Separate Single-Point Ground Systems
- Multi-Point Ground Systems
- Which Type of Ground
- Common Impedance Coupling
- Hybrid Grounds
- Separation of Grounds
- Low-Level Circuit
- Single-Ground Reference
- Amplifier Shields
- Signal Input to a Shield Enclosure
- Mutual Capacitance Between Shield and Ground
- Shield Connection
- Grounding of Cable Shield with Amplifier Grounded (low frequency)
- Grounding of Cable Shield with Grounded Source (low frequency)
- Low Frequency Grounding Schemes
- Ground Loops
- Ground Loop Isolation
- Transformer Ground Loop Isolation
- Common-Mode Choke Isolation
- How to Make a Common-Mode Choke
- Optical Coupler Isolation
- Balanced Circuit Isolation
- Shield Grounding at High Frequencies
Chapter 7 - Common Mode Rejection
- Problem .. Induced Noise
- Problem: Measure Small Voltage Differences In a High Common-Mode Environment.
- Shield Connection
- Amplifiers
- Amplifiers ..Common-Mode Rejection
- Differential Amplifiers
- "Normal-Mode" Voltage
- Common Mode Voltage
- Common Mode Error
- Common Mode Rejection Ratio
- Objective .. Reduce the Effects of Induced Noise
- Noise Rejection .. Differential Input
- Twisted Pair Conductors
- Shielding
- Shield Connection Strategies
- Shield Termination
- Driven Shield
- Amplifier Common
- Full Bridge
- Thermocouples
- The Real Differential Amplifier (and Source)
- Real Differential Amplifier & Source .. Effect
- Common Mode Rejection .. Source Impedance/Imbalance/Frequency Effects
Chapter 8 - (optional) Guarded Voltmeter
- Guard Shields
- Grounded Measurement
- Grounded Measurement with a Common-mode Voltage
- Floating Measurements
- Inside an Ideal Floating Voltmeter
- More Realistic View of a Floating Voltmeter
- Guarded Voltmeter
- Connecting the Guard
- Guard Connection to Low at Voltmeter
- Guard Connected to Earth Ground
- Bridge Measurement
- Guard connected to Low at Voltmeter Input
- Guard Connected to Low at the Bridge
- Guard Connected to Ground at the Bridge
- Driving the Guard in a Bridge Measurement
Chapter 9 - Enclosure Shielding
- Measuring Shielding Effectiveness
- Absorption Loss
- Absorptive Component
- Reflection Loss
- Wave Impedance
- Material Characteristic Impedance
- Electric Fields
- Net Effectiveness for Electric Fields
- Magnetic Fields
- Re-reflection of Magnetic Fields
- Net Shielding Effectiveness For Magnetic Fields
- Shielding Low Frequency Magnetic Fields
- High-μ Materials
- μr vs. Frequency
- Mechanical Shock Can Degrade δ
- Saturation of μr
- Multi-Layer Shields
- Directing Magnetic Flux
- High-μ Shield Changes Flux Distribution
- Magnetic vs. Electric Circuits
- Reluctance of a Finite Element
- Resistive Analogue
- Shield Across Flux
- Magnetic Shielding Example
- Shield Along Flux
- U-Bracket
- Shield Forms Complete Magnetic Circuit
- Effect of Shield Discontinuities
- Direction of Induced Current
- Slot Antennas Excited by Surface Currents
- Seam Orientation
- Aperture Shielding Effectiveness
- Screen Wire Over on Aperture
- Waveguide Below Cutoff
- Transfer Impedance
- Inducing Fields on the Shielded Side
- Contact Resistance of Seams
- Effect of Applied Pressure
- Increase Seam Contact Area
- Conductive Gaskets
- Measurement of Gasket Transfer Impedance
- Plastics
- Cabling to Shields
- Ground Wires
- Entry Point Bypassing
- Concentric Feedthrough Capacitor
- RFI - Tight Feed Throughs
- Ribbon Cables
- Coaxial Cables
- Transformer Shielding
- Single Transformer Shield
- Single Center Tap Transformer Shield
- Double Electrostatic Shield
Chapter 10 - Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
- Static Generation
- The Triboelectric Series
- Magnitude of Charge
- How Much Voltage?
- Inductive Coupling
- Charge Storage
- Human Body Model
- Discharge into an Ideal Ground
- Effects of ESD
- Types of ESD Damage
- Common Myths about ESD
- ESD Prevention
- ESD Workstation
- ESD by Induction
- Voltage Response vs. Foot Movement
- ESD Protection in Equipment Design
- Direct Conduction
- Less Destructive Current Path
- Current Flow
- Discharge into an Inductive Ground
- Secondary Arcing
- Don‘t Float Metal Parts
- Insulating the Discharge
- Bleeding Charge from Plastic Parts
- Magnetic Coupling
- Electric Coupling
- ESD Coupling in Cables
- Cable Grounding
- Separate Ground Return Lead
- Low Impedance Cable Grounding Area
- ESD in Ribbon Cables
- Common-Mode Choke
- Protecting the Circuit or System from Static Discharge
- Interface Cables and ESD
- Guard Ring
Chapter 11 - Circuit Board Layout
- Behavior of Ground Impedance
- Initial Layout
- Termination
- When to Terminate
- Connectors
- Resets
- Quiet Designs
- I/O Circuits
- Test Early and Often
- Trace Discontinuities Cause Radiation
- Segment Ground and Power Planes?
- Critical Circuits
- Susceptibility
- Input/Output
- Keep EMI in Mind When Selecting Devices
- Red Flag—High-speed CMOS
- Board Design
- Five-five Rule for Multilayer Boards
- Ground Plane Miracle
- Image Plane Effect
- Placement of Signal Traces
- Embed the Traces?
- Parallel Planes
Chapter 12 - Switching Power Supplies
- Control of Conducted Emissions from Switching Power Supplies
- Rectifier Diode Recovery
- Recover time
- Capacitively-Coupled Ground Circuit
- Returning Stray Switching Current to Primary Common
- Conventional vs. Low-Emission Secondary Filter
- Transformer Resonance Snubbing
- Snubber Design
- Possible Snubber Locations
Chapter 13 - Final Review
Appendix A - Glossary of Terms
Appendix C - Reference: Typical Capacitances, Electrical isolation for accelerometers, EM Radiation Frequency Range
Appendix D - ESD: An EMI Problem
Summary
Final Review
Certificates for Successful Completion
Click for a printable course outline (pdf).
Revised 7/11/18
